Articles
ArticlesSpace-Based Solar Energy: Harnessing the Sun's Power from Orbit
Space-based solar energy (SBSE) is an innovative method of energy generation that involves collecting solar power in space and transmitting it to Earth. It overcomes terrestrial limitations such as atmospheric absorption and intermittency due to day-night cycles. SBSE systems utilize extensive solar arrays that convert solar radiation into electrical power, which is then transformed into microwave or laser beams to be wirelessly transmitted to Earth-based receiving stations. The primary challenge facing SBSE is the significant cost associated with the launch and maintenance of space infrastructure, despite reductions in launch expenses. Concerns exist regarding the transmission efficiency and environmental impacts of the technology. The European Space Agency (ESA) is investing in SBSE, examining its feasibility and benefits, with efforts geared towards enhancing solar panel efficiency, wireless transmission, and tackling the logistical hurdles of space construction. CALTECH's Space Solar Power Demonstrator (SSPD) project is testing fundamental SBSE components: high-efficiency solar cells, wireless power transmission, and deployable structures. Promising initial results have indicated progress in solar technology and wireless energy transmission efficiency, vital to the future of SBSE systems.
Read Full articleThe smart city puzzle: cities, platforms and service provider
Working in smart city projects requires to bring together different players in this very diverse eco-system, from IT to product suppliers, service providers, finance, social innovators and of course the cities with their various departments. A good way to start is looking at top notch smart city projects as well as knowledge, matchmaking and IT platforms.
Read Full articleHarnessing Carbon: Europe's Ambitious Plan for Industrial Carbon Management
The EU's industrial carbon management strategy aims for climate neutrality by 2050, targeting innovations in carbon capture and utilization (CCU), carbon capture and storage (CCS), and CO2 transport through a 19,000 km network. This transformative approach, fostering a carbon value chain, could generate €45-€100 billion and create 75,000-170,000 jobs by 2030, while positioning the EU as a global leader in carbon management technologies. The strategy emphasizes investment, R&D, public engagement, international cooperation, and regulatory development.
Read Full articleBusiness Value Through Industrial Symbiosis
A new framework evaluates industrial symbiosis, showing cost savings, revenue growth, risk reduction, and intangible benefits, advocating strategic partnerships and regulatory navigation for long-term sustainable advantage.
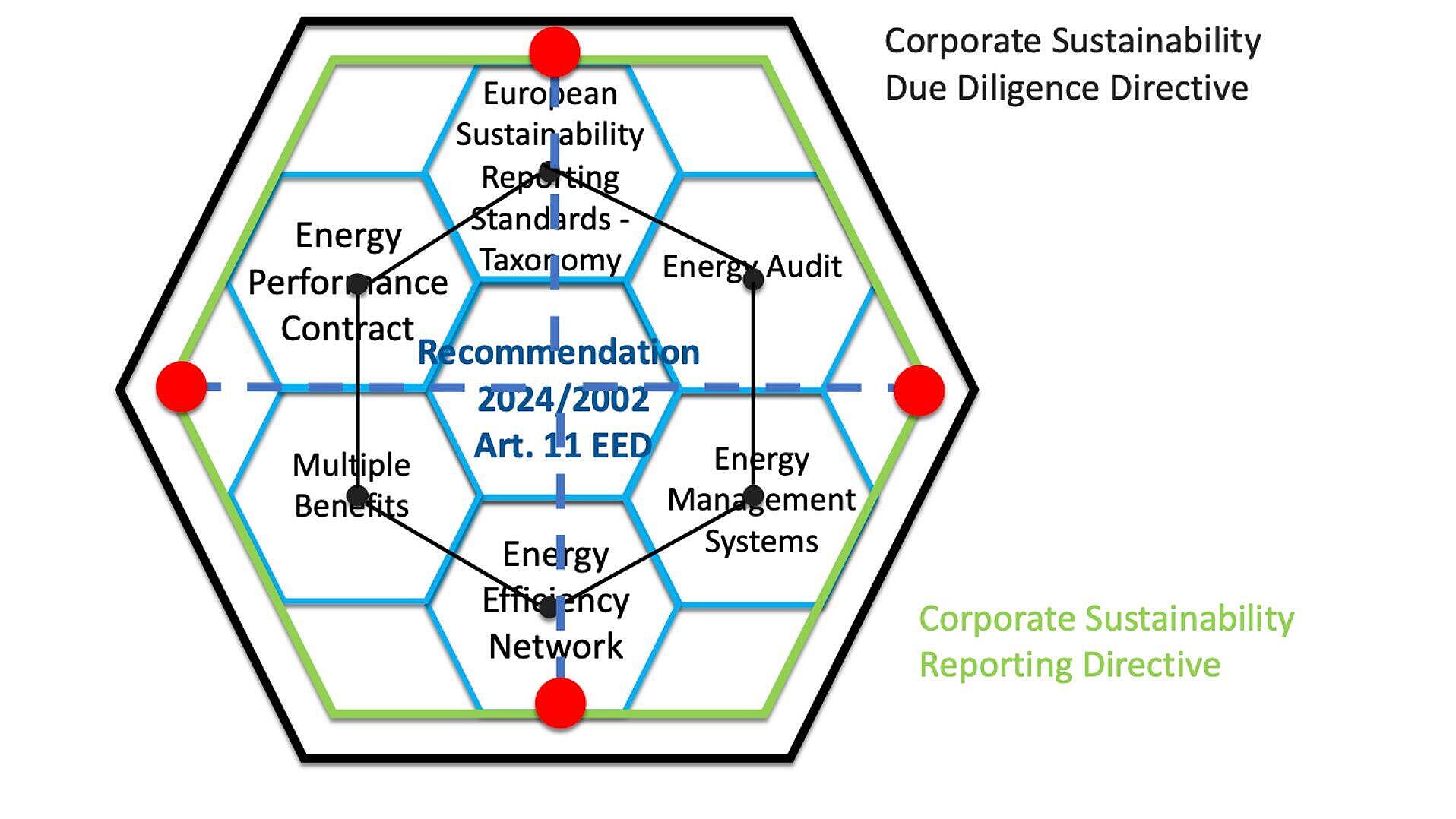
Read Full articleConnecting the dots of Energy Efficiency Directive with sustainable finance reporting. The full potential unlocked.
The European Commission issued guidelines to aid EU member states in adopting the Energy Efficiency Directive by October 2025. Recommendation 2024/2002 promotes an integrated approach to energy audits, management systems, and sustainability reporting, supporting compliance with broader EU directives.
Read Full articleCharging Ahead: How Electric Vehicles Are Powering a Sustainable Future for the Next Generation of Innovators
The paper discusses the rapid global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), driven by falling battery costs, government incentives, and a growing commitment to environmental sustainability. Advances in technology, like solid-state batteries and Vehicle-to-Grid systems, are enhancing EV capabilities and integration into energy grids. Despite challenges like charging infrastructure and ethical material sourcing, EVs are increasingly seen as crucial for cleaner transportation and climate change mitigation, impacting energy systems, creating new economic opportunities, and transforming urban environments.
Read Full articleTransforming Europe's Energy Grids for a Sustainable Future
The paper discusses Europe's transition to an interconnected, renewable-focused energy grid, emphasizing the need for smart grids, AI, flexibility markets, advanced data exchange, and interoperability. These elements are crucial for balancing supply and demand, enhancing grid efficiency, and achieving sustainability and decarbonization goals, all while facing challenges in technology, investment, and stakeholder collaboration.
Read Full articleHow Global Energy Investment Transformed from 2019 to 2025
From 2019 to 2025, global energy investment shifted dramatically towards clean energy, with investments doubling and surpassing fossil fuels. Solar power, driven by cost declines and technological advances, became the largest investment segment. However, while investment in renewables aligned with climate goals, grid investments lagged, creating bottlenecks. Surprisingly, AI data centers increased demand for reliable baseload power, reviving interest in nuclear and gas. Distributed solar grew in emerging markets independently of policy, reshaping economic dynamics, yet clean energy deployment remained unequal globally.
Read Full articleDigital Supply Chain Dynamics: Insights from Indonesia’s Food and Beverage Industry
The study explores how digitalization enhances operational performance in Indonesia's food and beverage sector, stressing improvements in quality, productivity, and cost efficiency through technologies like IoT, robotics, cloud computing, and blockchain.
Read Full article3 ways AI can support energy management
There are several ways that AI can be used to support energy management. The field of AI for energy efficiency is an active area of research and development, and new applications are being discovered all the time.
Read Full article