Policy & Regulation
Policy & RegulationPolicy & Regulation
The 2025 Energy Pivot: Navigating Europe's New Compliance Landscape for Business
Europe’s energy policy shift culminates in 2025, when major EU directives move from negotiation into national laws that create concrete compliance duties for businesses. The recast Energy Efficiency Directive turns “Energy Efficiency First” into a legal requirement and replaces size-based obligations with energy-consumption thresholds: firms above 10 TJ must conduct energy audits, and those above 85 TJ must implement energy management systems. In parallel, RED III raises the 2030 renewables target to 42.5% (aspiring to 45%) and tackles the biggest practical barrier—permitting—by introducing renewables acceleration areas with time-capped approvals and treating renewable projects as overriding public interest. Industry also faces binding requirements to increase renewable energy use by 1.6% annually, including uptake of RFNBOs such as green hydrogen. Looking beyond 2025, attention shifts to grid constraints and tougher 2040 climate targets.
Read Full articleHarnessing Carbon: Europe's Ambitious Plan for Industrial Carbon Management
The EU's industrial carbon management strategy aims for climate neutrality by 2050, targeting innovations in carbon capture and utilization (CCU), carbon capture and storage (CCS), and CO2 transport through a 19,000 km network. This transformative approach, fostering a carbon value chain, could generate €45-€100 billion and create 75,000-170,000 jobs by 2030, while positioning the EU as a global leader in carbon management technologies. The strategy emphasizes investment, R&D, public engagement, international cooperation, and regulatory development.
Read Full articleConnecting the dots of Energy Efficiency Directive with sustainable finance reporting. The full potential unlocked.
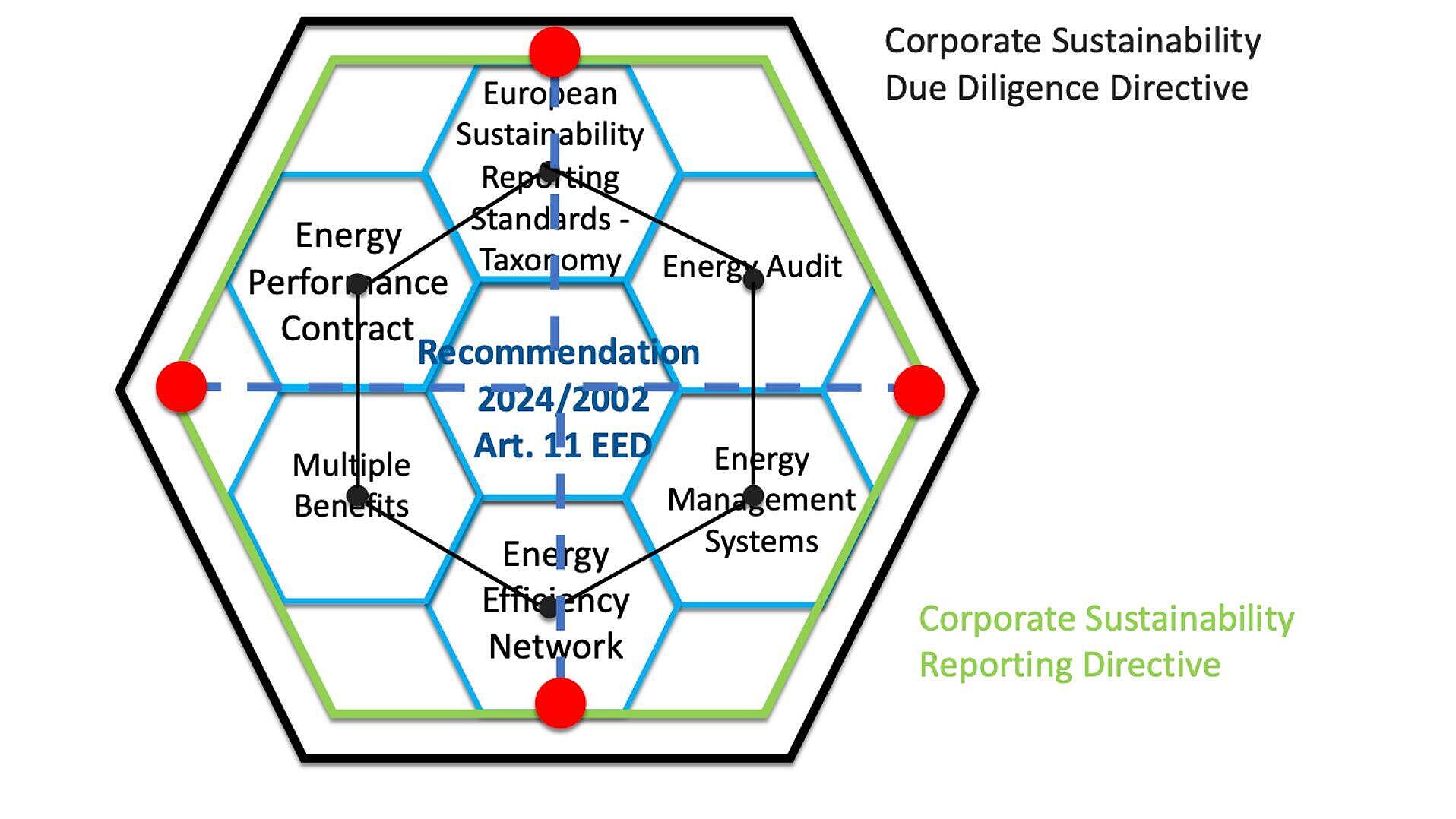
The European Commission issued guidelines to aid EU member states in adopting the Energy Efficiency Directive by October 2025. Recommendation 2024/2002 promotes an integrated approach to energy audits, management systems, and sustainability reporting, supporting compliance with broader EU directives.
Read Full articlePowering Europe's Clean Energy Future: Key Elements of the EU Energy Efficiency Directive
The EU Energy Efficiency Directive sets binding targets to reduce energy use by 2030 and introduces measures across sectors for energy savings, prioritizing efficiency, sustainability, and enhanced energy security for European citizens and businesses, requiring member states to implement various efficiency strategies and reporting mechanisms.
Read Full articleRevolutionizing Urban Living: Insights from the STARDUST Project
The STARDUST project exemplifies sustainable urban transformation through smart integration in energy, mobility, and ICT in "lighthouse" and "follower" cities, focusing on renewable infrastructure, innovative technologies, regulatory adaptability, stakeholder engagement, and novel business models to foster replicable sustainable city initiatives.
Read Full articleRevitalizing Europe's Industrial Future: The European Commission's Strategic Vision for 2024-2029
The European Commission's strategy for 2024-2029 aims to revitalize Europe's industrial sector, address economic challenges, promote sustainability, advance technological sovereignty, ensure social fairness, and strengthen global partnerships for a resilient, prosperous EU future.
Read Full articleThe Renewable Revolution: Powering Our Future
Studies outline scenarios for a 100% renewable energy system by 2050, emphasizing electrification, solar and wind dominance, job creation, grid flexibility, energy storage importance, green hydrogen's role, and socio-economic benefits including health and employment gains.
Read Full articleDoubling Energy Efficiency Progress: A Key to Achieving Climate Goals and Energy Security
The IEA's Energy Efficiency 2023 report calls for doubling global efficiency efforts to 4% annually for achieving net zero targets, highlighting significant regional progress, job creation potential, and the necessity for a transformative industry shift, supported by robust policies and investment.
Read Full articleAccelerating the Clean Energy Transition: An Updated Roadmap to Net Zero Emissions
The IEA's 2023 Net Zero Roadmap update outlines steps for a 1.5°C-aligned energy transition, emphasizing rapid clean energy deployment and innovation. It sets key 2030 milestones, including tripling renewables, improving efficiency, increasing EV sales, and reducing methane emissions. Global cooperation and investment are critical.
Read Full articleTop 10 EU Initiatives for Digitalizing the Energy System: Transforming Europe’s Energy Landscape
The European Union is advancing the digitalization of its energy infrastructure through 10 key initiatives that address data interoperability, grid management, cybersecurity, energy efficiency, and consumer empowerment to support its 2030 and 2050 climate goals. These initiatives aim to create an integrated, sustainable energy system that incorporates renewable energy and encourages innovation, while grappling with standardization and fast-paced digital innovation challenges.
Read Full article