Energy Efficiency
is connected
Energy Efficiency
is connected
EEIP, a global energy transition platform, is seeking a Team Leader for their EU Project Office to manage a team and the operations of various EU-funded projects. The role includes representing EEIP in project consortia, planning and reporting activities, identifying new EU funding opportunities, and handling financial management. The projects cover energy transition areas such as energy efficiency finance, smart cities, renewables, and clean fuels. Responsibilities also involve coordinating team tasks, capturing project learnings, implementing AI strategies, and leading project communication and knowledge transfer activities. The ideal candidate should have at least 5 years of relevant EU project experience, team management skills, knowledge in energy and sustainability, strong administrative abilities, and proficiency in English and another European language. Flexibility in work schedule and readiness to travel are essential. Applicants with the legal right to work in Belgium should submit their CV and cover letter by July 6, 2025.
Read Full articleHow Global Energy Investment Transformed from 2019 to 2025
From 2019 to 2025, global energy investment shifted dramatically towards clean energy, with investments doubling and surpassing fossil fuels. Solar power, driven by cost declines and technological advances, became the largest investment segment. However, while investment in renewables aligned with climate goals, grid investments lagged, creating bottlenecks. Surprisingly, AI data centers increased demand for reliable baseload power, reviving interest in nuclear and gas. Distributed solar grew in emerging markets independently of policy, reshaping economic dynamics, yet clean energy deployment remained unequal globally.
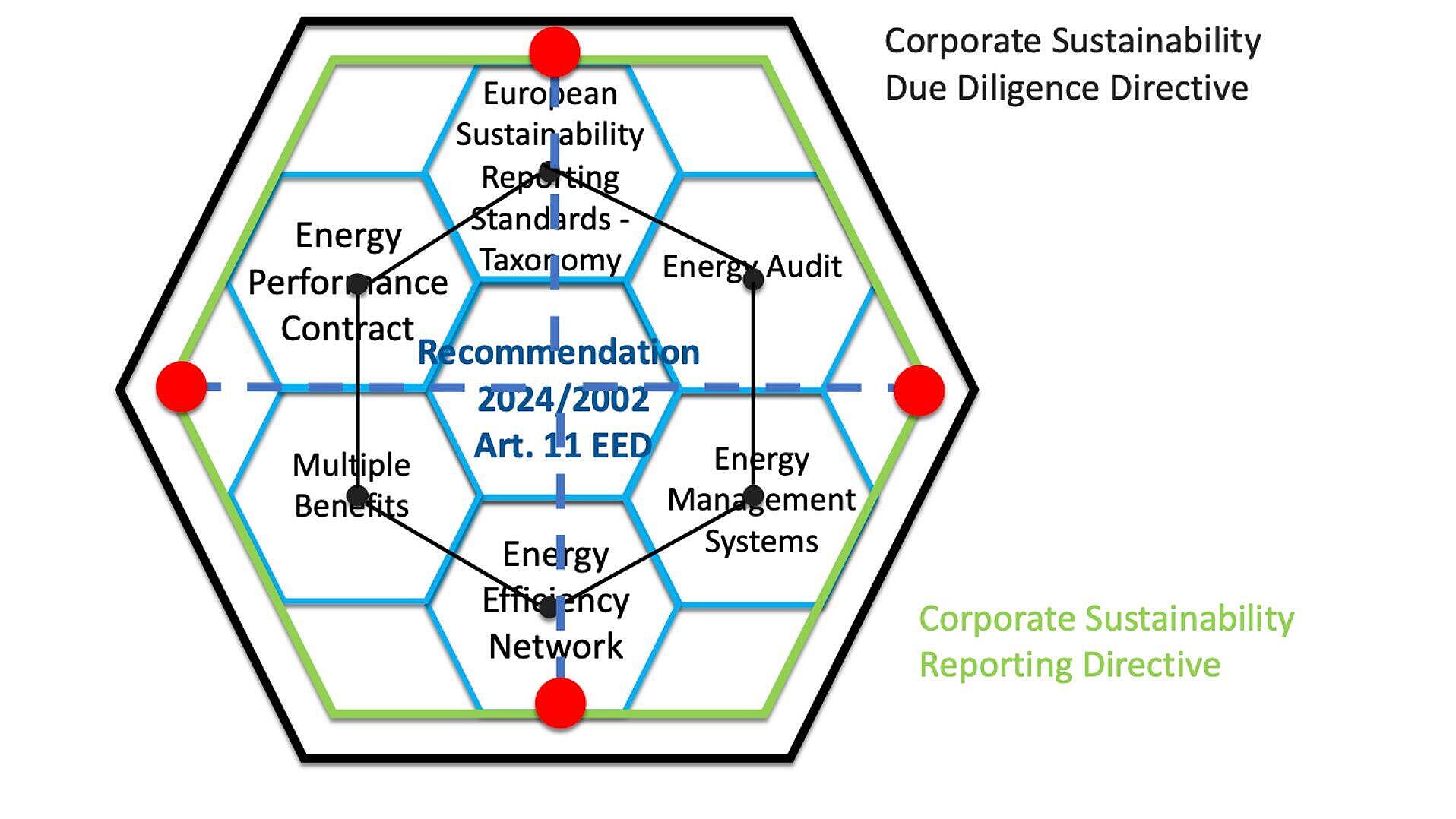
Read Full articlePowering Europe's Clean Energy Future: Key Elements of the EU Energy Efficiency Directive
The EU Energy Efficiency Directive sets binding targets to reduce energy use by 2030 and introduces measures across sectors for energy savings, prioritizing efficiency, sustainability, and enhanced energy security for European citizens and businesses, requiring member states to implement various efficiency strategies and reporting mechanisms.
Read Full articleBusiness Value Through Industrial Symbiosis
A new framework evaluates industrial symbiosis, showing cost savings, revenue growth, risk reduction, and intangible benefits, advocating strategic partnerships and regulatory navigation for long-term sustainable advantage.
Read Full article⚙ Business Practices
ORC-systems are helping to create a sustainable energy future
Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) technology is being used in Sweden to transform waste heat into renewable electricity. The high efficiency and low maintenance way to produce sustainable electricity is being adopted by district heating systems around the world. Read how Ronneby.
Read Full Business PracticeRank Organic Rankine Cycle Technology with applications in Heat Recovery solution
ORC RANK has worked with SWEP to implement a heat recovery solution for electricity power generation. The activation range for the low-temperature equipment starts at just 85 °C. SWEPs heat exchangers are installed as economizers,.
Read Full Business Practice