Energy Efficiency
is connected
Energy Efficiency
is connected
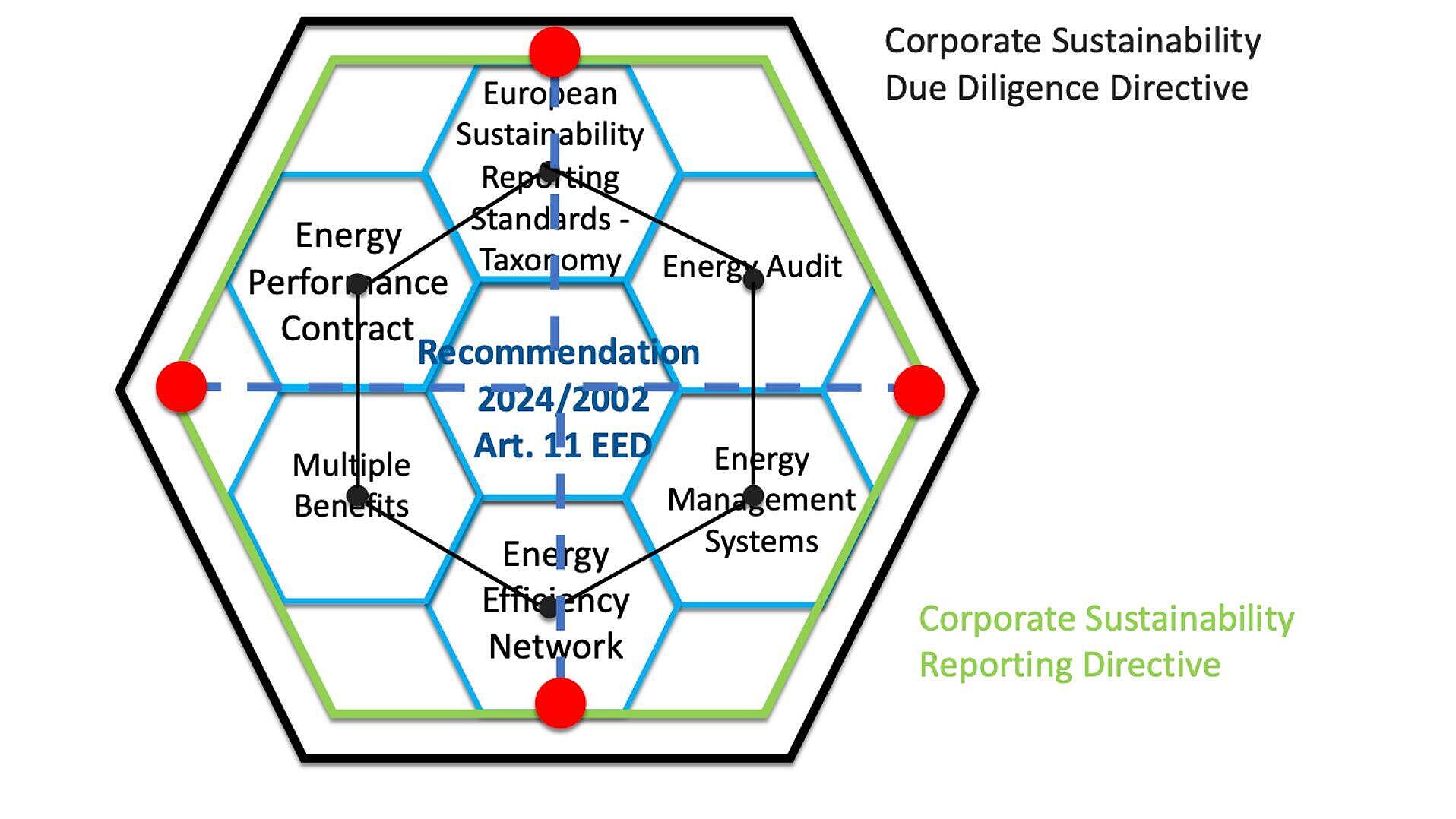
The DEESME Multiple Benefits Approach is a method aimed at boosting energy efficiency in European SMEs by recognizing broader business benefits rather than focusing solely on energy cost savings. Developed under the EU's Horizon 2020 program, DEESME advocates for energy audits and management systems that identify additional benefits like increased productivity, reduced environmental impact, improved health and safety, stronger brand reputation, compliance, and employee satisfaction. This approach involves four stages, starting with a Business Analysis that aligns energy efficiency with business priorities. The Energy Analysis focuses on energy usage data, followed by a Multiple Benefits Analysis to identify and measure extra financial, environmental, social, and reputational benefits from efficiency measures. The final stage is Business Model Sustainability Advancement, where the business integrates the findings into its model for sustainable growth, often resulting in innovation and improved sustainability communication. The DEESME approach emphasizes skill-building and team engagement across various company departments. It uses case studies to illustrate the multiplicative effects of integrating energy efficiency with broader business improvements. This strategy prepares businesses for future EU policies, sustainable finance opportunities, attracting talent, and comprehensive regulatory compliance. It's also supported by interactive materials and tools like Enerwhizz, an educational mobile quiz game designed to foster knowledge and competitiveness in energy management.
Read Full articleGame Changer: How Energy Audits are Transforming Small Businesses
Energy audits are becoming vital for SMEs in Europe, offering detailed analysis of energy usage and efficiency, highlighting cost-saving measures. They notably influence investment decisions in energy-efficient technologies, with smaller firms and innovative companies benefitting the most. However, financial constraints remain a barrier to implementing energy-saving opportunities.
Read Full articlePowering the Future: A Comprehensive Look at Hydrogen Production Methods
The paper provides an analysis of 19 hydrogen production methods, focusing on efficiency, cost, and environmental sustainability. It identifies the efficiency of fossil fuel reforming and the high environmental impact of non-renewable sources. Renewable methods are more sustainable but less developed. Hybrid approaches offer balanced results while further innovation is needed for truly sustainable hydrogen production.
Read Full articleInnovative financial solutions to fight energy poverty
How social housing associations and EU projects are using innovative financial and solidarity mechanisms to combat energy poverty, emphasizing the dual benefit of social welfare and environmental sustainability through the refurbishment of buildings for energy efficiency.
Read Full article⚙ Business Practices
ORC-systems are helping to create a sustainable energy future
Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) technology is being used in Sweden to transform waste heat into renewable electricity. The high efficiency and low maintenance way to produce sustainable electricity is being adopted by district heating systems around the world. Read how Ronneby.
Read Full Business PracticeRank Organic Rankine Cycle Technology with applications in Heat Recovery solution
ORC RANK has worked with SWEP to implement a heat recovery solution for electricity power generation. The activation range for the low-temperature equipment starts at just 85 °C. SWEPs heat exchangers are installed as economizers,.
Read Full Business Practice